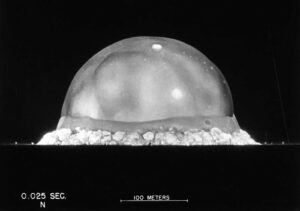
1945 in the desert north of Alamogordo, New Mexico, the first nuclear test took place, code-named ‘Trinity’. The test released energy equivalent to 22 kilotons of TNT, far more powerful than any weapon ever used before.
1945 Three weeks later the US dropped two atomic bombs on the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan killing over 200,000 people.
1949 the Soviet Union conducted its first nuclear test explosion. Followed by the UK (1952), France (1960), and China (1964).
1968 Nuclear proliferation was an early concern of the Cold War, and the fear of nuclear war led to the nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT). Non-nuclear weapon states agree never to acquire nuclear weapons, and those states with nuclear weapons make a legal undertaking to disarm.
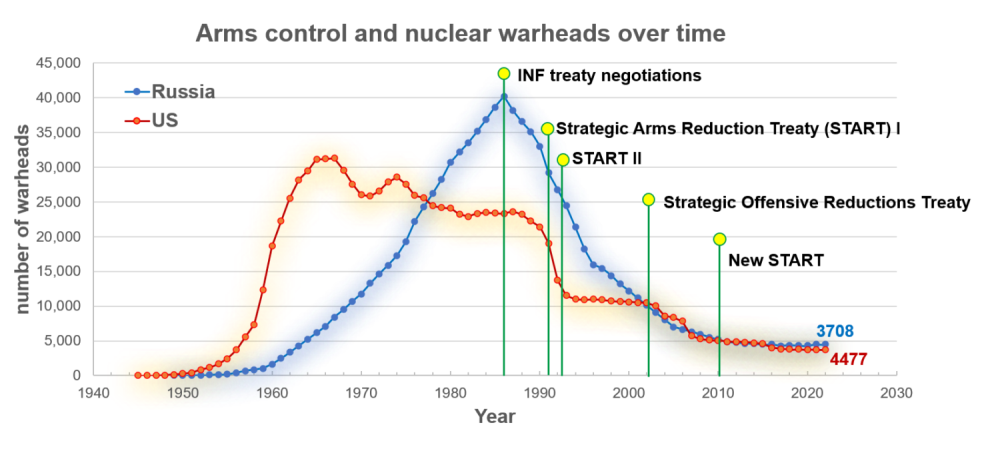
At the time the NPT was concluded, the nuclear stockpiles of both the United States and the Soviet Union/Russia numbered in the tens of thousands.
1970s, US and Soviet/Russian leaders negotiated a series of bilateral arms control agreements and initiatives that limited, and later helped to considerably reduce the size of their nuclear arsenals.
China’s nuclear stockpile increased until the early 1980s when it stabilized at between 200 and 260. India became a nuclear power in 1974, while Pakistan developed its first nuclear weapon in the 1980s.
1987 The US and Soviet Union signed the Intermediate – range Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF) to eliminate land-based missiles and employ on-site inspections. In 2019 the Trump administration withdrew from the INF treaty.
1996 A total nuclear test ban treaty Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (CTBT) prohibited any nuclear weapon test explosion, or any other nuclear explosion, anywhere in the world. It has been signed by 187 nations and ratified by 177. It cannot enter into force until it is ratified by 44 specific nations, 9 of which must still do so.
India, Israel, and Pakistan possess nuclear arsenals. Iraq initiated a secret nuclear program under Saddam Hussein before the 1991 Persian Gulf War. North Korea announced its withdrawal from the NPT in January 2003 and has tested advanced nuclear devices since that time. Iran and Libya have pursued secret nuclear activities in violation of the treaty’s terms, and Syria is suspected of having done the same.
114 states have established themselves as Nuclear-weapon free zones covering 39% of the world’s population. This includes Latin America and the Caribbean , Central Asia, Africa and the South Pacific. 47% are nuclear weapon states, 14% are neither.
More recently…
2017 The UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons was adopted, and entered into force Jan 2021. It is the first legally binding international agreement to comprehensively prohibit nuclear weapons, with the ultimate goal being their total elimination.
2021 the New START agreement was extended for 5 years and both the U.S. and Russia have committed to the treaty’s central limits on strategic force deployments until 2026. In 2023 Russia suspended its participation but did not withdraw from the treaty.
Currently, the US, Russia, and China also possess smaller numbers of non-strategic (or tactical) nuclear warheads, which are shorter-range, lower-yield weapons that are not subject to any treaty limits.
Further Reading
- CND: International Agreements Relating To Nuclear Weapons
- Arms Control Association
- Union of Concerned Scientists Arms Control and warheads over time.
- ICAN: Nuclear weapon history
